最近做一个小程序开发任务,主要负责后台部分开发;根据项目需求需要实现三个定时任务: 1>定时更新微信token,需要2小时更新一次; 2>商品定时上线; 3>定时检测后台服务是否存活; 使用Python去实现这三个任务,这里需要使用定时相关知识点; Python实现定点与定时任务方式比较多,找到下面四中实现方式,每个方式都有自己应用场景;下面来快速介绍Python中常用的定时任务实现方式: 1>循环+sleep;…
Python 数据类型, Python3 基本数据类型, Python Data Types

数据类型是数据项的分类或分类。它表示一种值,它告诉可以对特定数据执行哪些操作。由于在 Python 编程中一切都是对象,因此数据类型实际上是类,而变量是这些类的实例(对象)。
以下是 Python 的标准或内置数据类型:
内置数据类型
在编程中,数据类型是一个重要的概念。
变量可以存储不同类型的数据,并且不同类型可以执行不同的操作。
在这些类别中,Python 默认拥有以下内置数据类型:
| 文本类型: | str |
| 数值类型: | int, float, complex |
| 序列类型: | list, tuple, range |
| 映射类型: | dict |
| 集合类型: | set, frozenset |
| 布尔类型: | bool |
| 二进制类型: | bytes, bytearray, memoryview |
标准数据类型
Python3 中有六个标准的数据类型:
- Number(数字)
- String(字符串)
- List(列表)
- Tuple(元组)
- Set(集合)
- Dictionary(字典)
Python3 的六个标准数据类型中:
- 不可变数据(3 个):Number(数字)、String(字符串)、Tuple(元组);
- 可变数据(3 个):List(列表)、Dictionary(字典)、Set(集合)。
获取数据类型
您可以使用 type() 函数获取任何对象的数据类型:
- Numeric (数字)
- Sequence Type (序列类型)
- Boolean (布尔值)
- Set (集合)
- Dictionary (字典)
Numeric 数字
在 Python 中,数值数据类型表示具有数值的数据。数值可以是整数、浮点数甚至复数。这些值在 Python中定义为int,float 和 complex class。
- Integers 整数– 此值由 int 类表示。它包含正整数或负整数(没有小数或小数)。在 Python 中,整数值的长度没有限制。
- Float 浮点数 – 此值由浮点类表示。它是一个带有浮点表示的实数。它由小数点指定。可选地,可以附加字符 e 或 E 后跟一个正整数或负整数以指定科学记数法。
- Complex Numbers 复数——复数由复数类表示。它被指定为(real part) + (imaginary part)j。例如 – 2+3j
注–type()函数用于确定数据类型的类型。
# Python program to
# demonstrate numeric value
a = 5
print("Type of a: ", type(a))
b = 5.0
print("\nType of b: ", type(b))
c = 2 + 4j
print("\nType of c: ", type(c))
Output:
Type of a: <class 'int'> Type of b: <class 'float'> Type of c: <class 'complex'>
Sequence Type 序列类型
在 Python 中,序列是相似或不同数据类型的有序集合。序列允许以有组织和有效的方式存储多个值。Python中有几种序列类型——
- String 字符串
- List 列表
- Tuple 元组
1) String 字符串
在 Python 中,字符串是表示 Unicode 字符的字节数组。字符串是放在单引号、双引号或三引号中的一个或多个字符的集合。在 python 中没有字符数据类型,字符是长度为 1 的字符串。它由str 类表示。
创建字符串
Python 中的字符串可以使用单引号或双引号甚至三引号来创建。
# Python Program for
# Creation of String
# Creating a String
# with single Quotes
String1 = 'Welcome to the Geeks World'
print("String with the use of Single Quotes: ")
print(String1)
# Creating a String
# with double Quotes
String1 = "I'm a Geek"
print("\nString with the use of Double Quotes: ")
print(String1)
print(type(String1))
# Creating a String
# with triple Quotes
String1 = '''I'm a Geek and I live in a world of "Geeks"'''
print("\nString with the use of Triple Quotes: ")
print(String1)
print(type(String1))
# Creating String with triple
# Quotes allows multiple lines
String1 = '''Geeks
For
Life'''
print("\nCreating a multiline String: ")
print(String1)
输出:
String with the use of Single Quotes:
Welcome to the Geeks World
String with the use of Double Quotes:
I'm a Geek
<class 'str'>
String with the use of Triple Quotes:
I'm a Geek and I live in a world of "Geeks"
<class 'str'>
Creating a multiline String:
Geeks
For
Life
单引号和双引号是互相补充:
原始字符串中包含单引号,可以使用双引号定义;
原始字符串中包含双引号,可以使用单引号定义;
当用单引号包起来的字符串里包含”的时候, 不需要使用转义符(\), 反过来也是一样。当然你也可以继续使用转义符,对字符串中的单引号或双引号进行转义,不过代码的可读性就变糟糕了。
三引号:由三个成对的单引号或者三个成对的双引号组成 。主要有2大用法。
多行注释:
这个就不多说了,当文档注释有很多行时候,用这个非常方便。#通常是单行注释,但是注释有多行时,用三引号可以一次性解决 。
"""
这是一个
多行注释
"""
print('Hello world!')
定义多行字符串:
三引号包含的字符串可由多行组成,可以直接换行,不需要使用“\n”,字符串内容有单引号、双引号时也不需要进行转义。
# 三单引号(''')
print('''hello
world
python''')
# 三双引号(""")
print("""hello
world
python""")
输出都是
hello
world
python
访问 String 的元素
在 Python 中,可以使用 Indexing 方法访问 String 的各个字符。索引允许负地址引用从字符串后面访问字符,例如 -1 表示最后一个字符,-2 表示倒数第二个字符等等。

# Python Program to Access
# characters of String
String1 = "GeeksForGeeks"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
# Printing First character
print("\nFirst character of String is: ")
print(String1[0])
# Printing Last character
print("\nLast character of String is: ")
print(String1[-1])
输出:
Initial String: GeeksForGeeks First character of String is: G Last character of String is: s
#!/usr/bin/python3 str = 'Runoob' print (str) # 输出字符串 print (str[0:-1]) # 输出第一个到倒数第二个的所有字符 print (str[0]) # 输出字符串第一个字符 print (str[2:5]) # 输出从第三个开始到第五个的字符 print (str[2:]) # 输出从第三个开始的后的所有字符 print (str * 2) # 输出字符串两次,也可以写成 print (2 * str) print (str + "TEST") # 连接字符串
2) List 列表
List列表就像数组一样,用其他语言声明,是有序的数据集合。它非常灵活,因为列表中的项目不需要属于同一类型。
变量[头下标:尾下标]
索引值以 0 为开始值,-1 为从末尾的开始位置。
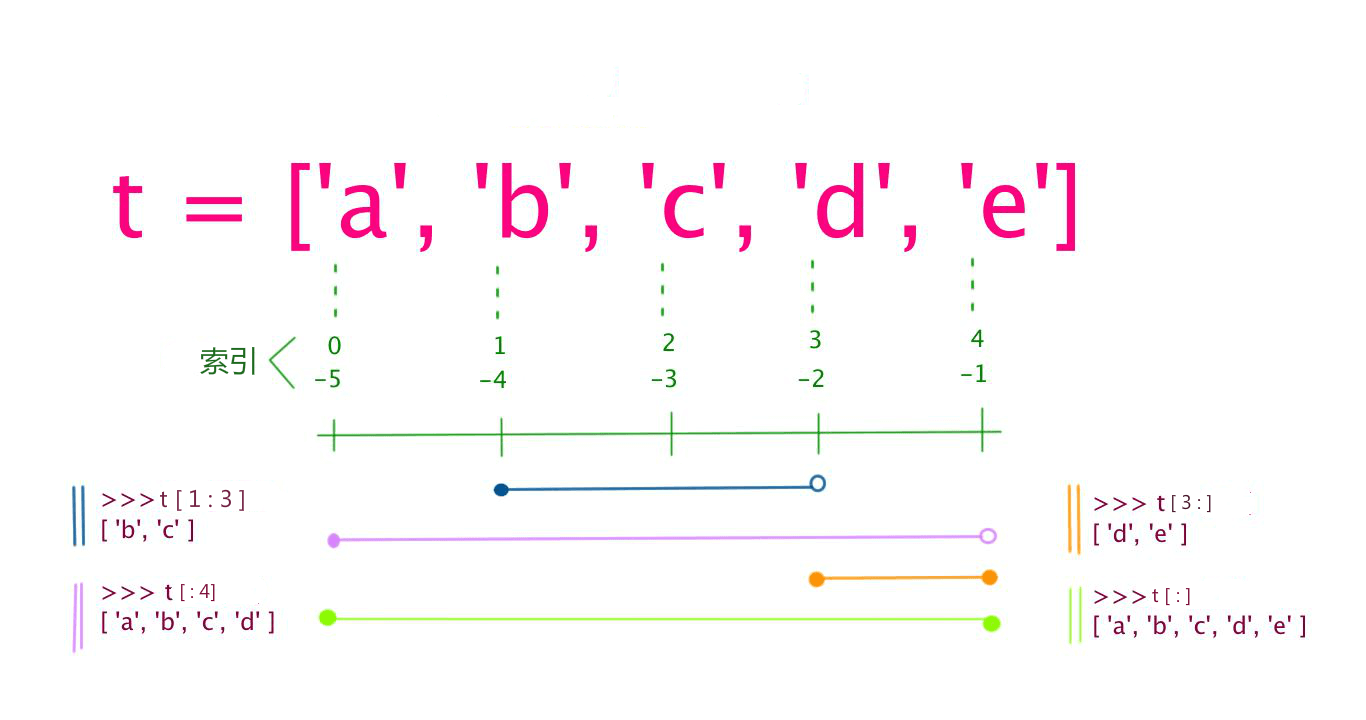
创建列表
Python 中的列表只需将序列放在方括号内即可创建[]。
# Python program to demonstrate
# Creation of List
# Creating a List
List = []
print("Initial blank List: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List with
# the use of a String
List = ['GeeksForGeeks']
print("\nList with the use of String: ")
print(List)
# Creating a List with
# the use of multiple values
List = ["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"]
print("\nList containing multiple values: ")
print(List[0])
print(List[2])
# Creating a Multi-Dimensional List
# (By Nesting a list inside a List)
List = [['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]
print("\nMulti-Dimensional List: ")
print(List)
输出:
Initial blank List: [] List with the use of String: ['GeeksForGeeks'] List containing multiple values: Geeks Geeks Multi-Dimensional List: [['Geeks', 'For'], ['Geeks']]
访问 List 的元素
为了访问列表项,请参阅索引号。使用索引运算符[ ]访问列表中的项目。在 Python 中,负序索引表示从数组末尾开始的位置。不必像 中那样计算偏移量List[len(List)-3],只需编写List[-3]. 负索引表示从末尾开始,-1 指最后一项,-2 指倒数第二项,依此类推。
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing of element from list
# Creating a List with
# the use of multiple values
List = ["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"]
# accessing a element from the
# list using index number
print("Accessing element from the list")
print(List[0])
print(List[2])
# accessing a element using
# negative indexing
print("Accessing element using negative indexing")
# print the last element of list
print(List[-1])
# print the third last element of list
print(List[-3])
输出:
Accessing element from the list Geeks Geeks Accessing element using negative indexing Geeks Geeks
#!/usr/bin/python3 list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'runoob', 70.2 ] tinylist = [123, 'runoob'] print (list) # 输出完整列表 print (list[0]) # 输出列表第一个元素 print (list[1:3]) # 从第二个开始输出到第三个元素 print (list[2:]) # 输出从第三个元素开始的所有元素 print (tinylist * 2) # 输出两次列表 print (list + tinylist) # 连接列表
3) Tuple 元组
就像列表一样,元组也是 Python 对象的有序集合。元组和列表之间的唯一区别是元组是不可变的,即元组在创建后不能修改。它由tuple 类表示。
创建元组
在 Python 中,通过放置由“逗号”分隔的值序列来创建元组,可以使用或不使用括号对数据序列进行分组。元组可以包含任意数量的元素和任何数据类型(如字符串、整数、列表等)。
注意:也可以使用单个元素创建元组,但这有点棘手。括号中只有一个元素是不够的,必须有一个尾随的“逗号”才能使其成为一个元组。
# Python program to demonstrate
# creation of Set
# Creating an empty tuple
Tuple1 = ()
print("Initial empty Tuple: ")
print (Tuple1)
# Creating a Tuple with
# the use of Strings
Tuple1 = ('Geeks', 'For')
print("\nTuple with the use of String: ")
print(Tuple1)
# Creating a Tuple with
# the use of list
list1 = [1, 2, 4, 5, 6]
print("\nTuple using List: ")
print(tuple(list1))
# Creating a Tuple with the
# use of built-in function
Tuple1 = tuple('Geeks')
print("\nTuple with the use of function: ")
print(Tuple1)
# Creating a Tuple
# with nested tuples
Tuple1 = (0, 1, 2, 3)
Tuple2 = ('python', 'geek')
Tuple3 = (Tuple1, Tuple2)
print("\nTuple with nested tuples: ")
print(Tuple3)
输出:
Initial empty Tuple:
()
Tuple with the use of String:
('Geeks', 'For')
Tuple using List:
(1, 2, 4, 5, 6)
Tuple with the use of function:
('G', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's')
Tuple with nested tuples:
((0, 1, 2, 3), ('python', 'geek'))
注意——不使用括号创建 Python 元组被称为元组打包。
访问元组的元素
为了访问元组项目,请参考索引号。使用索引运算符[ ]访问元组中的项目。索引必须是整数。使用嵌套索引访问嵌套元组。
# Python program to
# demonstrate accessing tuple
tuple1 = tuple([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Accessing element using indexing
print("First element of tuple")
print(tuple1[0])
# Accessing element from last
# negative indexing
print("\nLast element of tuple")
print(tuple1[-1])
print("\nThird last element of tuple")
print(tuple1[-3])
输出:
First element of tuple 1 Last element of tuple 5 Third last element of tuple 3
Boolean 布尔值
具有两个内置值之一的数据类型,True 或False。等于 True 的布尔对象为真 (true),等于 False 的布尔对象为假 (false)。但是非布尔对象也可以在布尔上下文中进行评估,并确定为真或假。它由类表示bool。
注意– 带有大写“T”和“F”的 True 和 False 是有效的布尔值,否则 python 会抛出错误。
# Python program to # demonstrate boolean type print(type(True)) print(type(False)) print(type(true))
输出:
<class 'bool'>
<class 'bool'>
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/7e8862763fb66153d70824099d4f5fb7.py", line 8, in
print(type(true))
NameError: name 'true' is not defined
Set 集合
在 Python 中,Set是数据类型的无序集合,它是可迭代的、可变的并且没有重复元素。集合中元素的顺序是不确定的,尽管它可能由各种元素组成。
创建集
可以通过使用带有可迭代对象或序列的内置set()函数来创建集合,方法是将序列放在花括号内,用“逗号”分隔。集合中元素的类型不必相同,也可以将各种混合的数据类型值传递给集合。
# Python program to demonstrate
# Creation of Set in Python
# Creating a Set
set1 = set()
print("Initial blank Set: ")
print(set1)
# Creating a Set with
# the use of a String
set1 = set("GeeksForGeeks")
print("\nSet with the use of String: ")
print(set1)
# Creating a Set with
# the use of a List
set1 = set(["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"])
print("\nSet with the use of List: ")
print(set1)
# Creating a Set with
# a mixed type of values
# (Having numbers and strings)
set1 = set([1, 2, 'Geeks', 4, 'For', 6, 'Geeks'])
print("\nSet with the use of Mixed Values")
print(set1)
输出:
Initial blank Set:
set()
Set with the use of String:
{'F', 'o', 'G', 's', 'r', 'k', 'e'}
Set with the use of List:
{'Geeks', 'For'}
Set with the use of Mixed Values
{1, 2, 4, 6, 'Geeks', 'For'}
访问集合的元素
集合项不能通过引用索引来访问,因为集合是无序的,这些项没有索引。但是您可以使用 for 循环遍历集合项,或者使用in 关键字询问集合中是否存在指定值。
# Python program to demonstrate
# Accessing of elements in a set
# Creating a set
set1 = set(["Geeks", "For", "Geeks"])
print("\nInitial set")
print(set1)
# Accessing element using
# for loop
print("\nElements of set: ")
for i in set1:
print(i, end =" ")
# Checking the element
# using in keyword
输出:
Initial set:
{'Geeks', 'For'}
Elements of set:
Geeks For
True
Dictionary 字典
Python 中的Dictionary是数据值的无序集合,用于像 map 一样存储数据值,与其他只保存单个值作为元素的 Data Types 不同,Dictionary 保存的是key:value pair。字典中提供了键值,使其更加优化。Dictionary 中的每个键值对由冒号分隔:,而每个键由“逗号”分隔。
创建字典
在 Python 中,可以通过在大括号内放置一系列元素来创建字典{},并用“逗号”分隔。字典中的值可以是任何数据类型并且可以重复,而键不能重复并且必须是不可变的。字典也可以通过内置函数创建 dict()。只需将其放在花括号{} 中即可创建一个空字典。
注意– 字典键区分大小写,相同名称但不同大小写的 Key 将被区别对待。
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Integer Keys
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Integer Keys: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Mixed keys
Dict = {'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with dict() method
Dict = dict({1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3:'Geeks'})
print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with each item as a Pair
Dict = dict([(1, 'Geeks'), (2, 'For')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
输出:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary with the use of Integer Keys:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with the use of Mixed Keys:
{1: [1, 2, 3, 4], 'Name': 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with the use of dict():
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with each item as a pair:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For'}
访问字典的元素
为了访问字典的项目,请参考它的键名。键可以在方括号内使用。还有一个称为的方法get()也将有助于从字典中访问元素。
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing a element from a Dictionary
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
# accessing a element using key
print("Accessing a element using key:")
print(Dict['name'])
# accessing a element using get()
# method
print("Accessing a element using get:")
print(Dict.get(3))
输出:
Accessing a element using key: For Accessing a element using get: Geeks
#!/usr/bin/python3
dict = {}
dict['one'] = "1 - 菜鸟教程"
dict[2] = "2 - 菜鸟工具"
tinydict = {'name': 'runoob','code':1, 'site': 'www.runoob.com'}
print (dict['one']) # 输出键为 'one' 的值
print (dict[2]) # 输出键为 2 的值
print (tinydict) # 输出完整的字典
print (tinydict.keys()) # 输出所有键
print (tinydict.values()) # 输出所有值
以上实例输出结果:
1 - 菜鸟教程
2 - 菜鸟工具
{'name': 'runoob', 'code': 1, 'site': 'www.runoob.com'}
dict_keys(['name', 'code', 'site'])
dict_values(['runoob', 1, 'www.runoob.com'])
Python数据类型转换
有时候,我们需要对数据内置的类型进行转换,数据类型的转换,你只需要将数据类型作为函数名即可,在下一章节 Python3 数据类型转换 会具体介绍。
以下几个内置的函数可以执行数据类型之间的转换。这些函数返回一个新的对象,表示转换的值。
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int(x [,base]) | 将x转换为一个整数 |
| float(x) | 将x转换到一个浮点数 |
| complex(real [,imag]) | 创建一个复数 |
| str(x) | 将对象 x 转换为字符串 |
| repr(x) | 将对象 x 转换为表达式字符串 |
| eval(str) | 用来计算在字符串中的有效Python表达式,并返回一个对象 |
| tuple(s) | 将序列 s 转换为一个元组 |
| list(s) | 将序列 s 转换为一个列表 |
| set(s) | 转换为可变集合 |
| dict(d) | 创建一个字典。d 必须是一个 (key, value)元组序列。 |
| frozenset(s) | 转换为不可变集合 |
| chr(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个字符 |
| ord(x) | 将一个字符转换为它的整数值 |
| hex(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个十六进制字符串 |
| oct(x) | 将一个整数转换为一个八进制字符串 |
本文:Python 数据类型, Python3 基本数据类型, Python Data Types
![]()






